Maintaining your car is not just about keeping it looking good; it’s about safety, performance, and longevity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into 15 essential car maintenance tasks that every driver should master to keep their vehicle running smoothly, efficiently, and safely.
1. Checking Fluid Levels
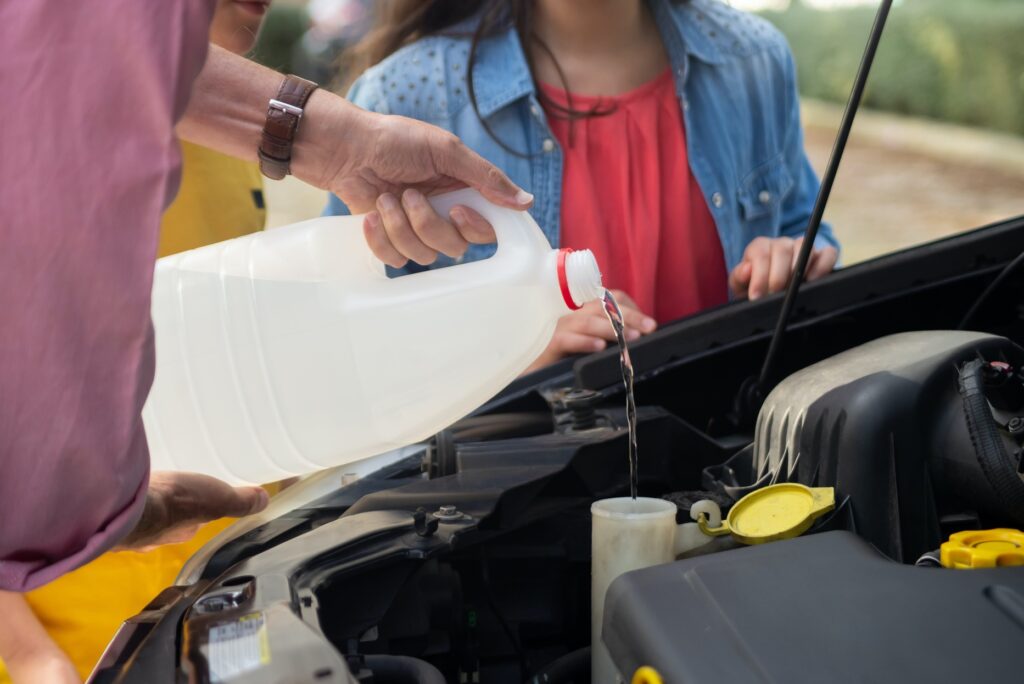

Regularly monitoring your car’s fluid levels is crucial for its overall health. Here’s what you need to know:
Engine Oil:
Engine oil lubricates the engine’s moving parts and helps dissipate heat. Check the oil level using the dipstick when the engine is cool and top up if necessary. Change the oil and oil filter as recommended by your vehicle manufacturer.
Coolant:
Coolant, also known as antifreeze, regulates engine temperature and prevents it from overheating or freezing. Check the coolant level in the reservoir and top up with a mixture of coolant and distilled water if needed. Inspect hoses for leaks or cracks and replace them if necessary.
Transmission Fluid:
Transmission fluid lubricates and cools the transmission system, ensuring smooth gear shifts. Check the transmission fluid level according to your vehicle manufacturer’s instructions and top up if needed. Consider having the transmission fluid flushed and replaced as part of regular maintenance.
Brake Fluid:
Brake fluid transfers force from the brake pedal to the brake calipers, enabling effective braking. Check the brake fluid level in the reservoir and top up with the recommended brake fluid if it’s low. Inspect the brake lines for leaks or damage and replace them if necessary.
Power Steering Fluid:
Power steering fluid enables easy steering by providing hydraulic assistance. Check the power steering fluid level regularly and top up if needed. Inspect the power steering system for leaks and repair any leaks promptly to prevent damage to the steering components.
Windshield Washer Fluid:
Maintaining clear visibility is essential for safe driving. Keep the windshield washer fluid reservoir topped up with a mixture of water and windshield washer fluid. Check washer nozzles for blockages and clean them if necessary to ensure proper windshield cleaning.
2. Inspecting Tire Pressure and Tread Depth
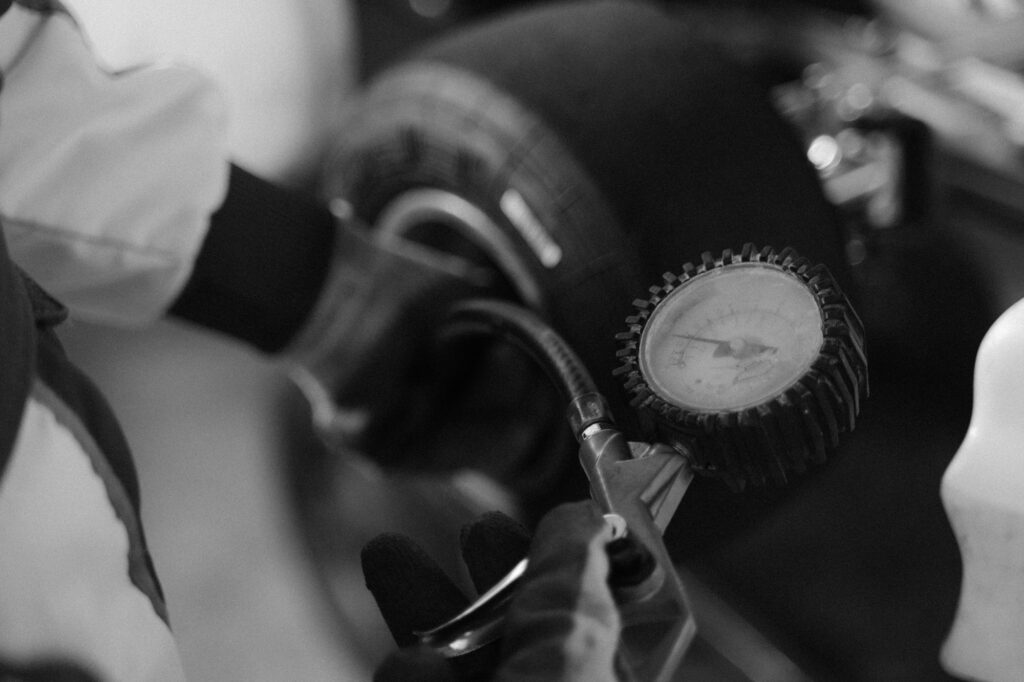

Your tires are the only contact points between your car and the road, so it’s crucial to keep them in good condition:
Tire Pressure:
Proper tire inflation ensures optimal handling, fuel efficiency, and tire lifespan. Use a tire pressure gauge to check tire pressure monthly, including the spare tire. Inflate tires to the recommended pressure listed in your vehicle owner’s manual or on the driver’s side door jamb.
Tire Tread Depth:
Tire tread depth affects traction and braking performance, especially in wet or snowy conditions. Measure tire tread depth regularly using a tread depth gauge or the penny test. Replace tires if the tread depth is worn down to 2/32 of an inch or less.
Tire Rotation:
Rotating tires regularly promotes even wear and extends tire lifespan. Follow the recommended rotation pattern outlined in your vehicle owner’s manual, typically rotating tires every 6,000 to 8,000 miles. Consider rotating tires more frequently if you notice uneven wear patterns.
Wheel Alignment:
Proper wheel alignment ensures even tire wear and optimal vehicle handling. Have the wheel alignment checked regularly, especially after hitting potholes or curbs. Signs of misalignment include uneven tire wear or steering wheel vibration.
Wheel Balancing:
Balanced wheels prevent vibration and ensure smooth vehicle operation. Have the wheels balanced whenever you install new tires, rotate tires, or notice steering wheel vibration. Proper wheel balancing improves tire longevity and overall driving comfort.
3. Replacing Air Filters
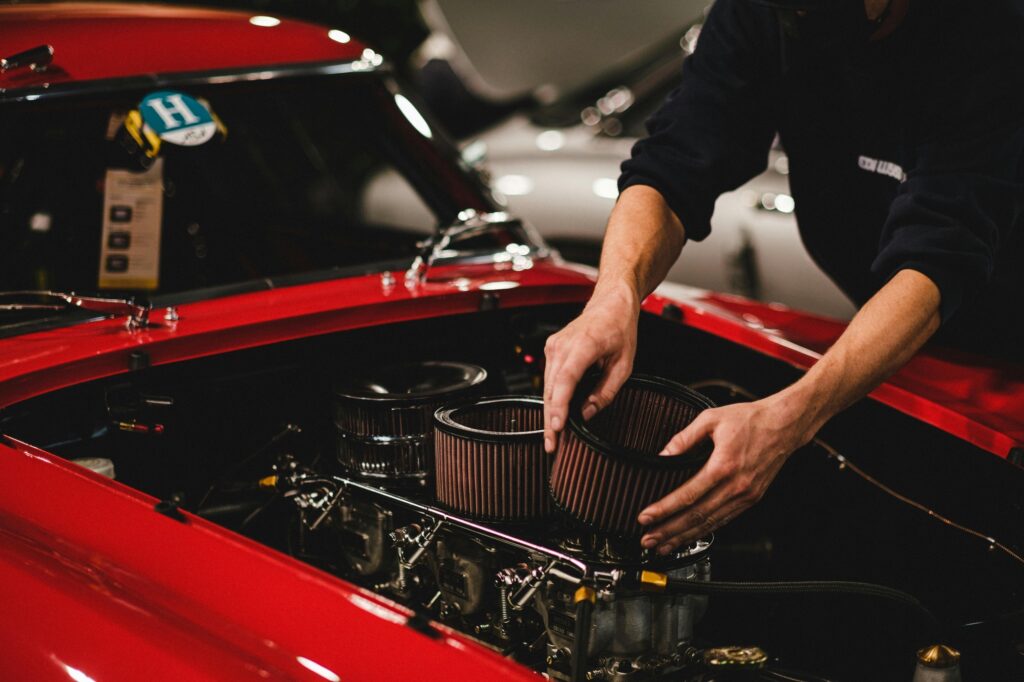

Clean air filters are essential for engine performance, fuel efficiency, and air quality inside the car:
Engine Air Filter:
The engine air filter prevents dirt and debris from entering the engine’s combustion chambers. Inspect the engine air filter regularly and replace it if it’s dirty or clogged. A dirty air filter restricts airflow, reducing engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Cabin Air Filter:
The cabin air filter removes dust, pollen, and other contaminants from the air entering the cabin. Replace the cabin air filter according to your vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations or if you notice reduced airflow or unpleasant odors inside the car. A clean cabin air filter improves air quality and HVAC system performance.
4. Testing Exterior Lights

Properly functioning exterior lights are essential for visibility and safety on the road:
Headlights:
Test headlights on low and high beams to ensure they illuminate properly. Replace any burnt-out bulbs promptly, and aim headlights correctly to prevent glare for other drivers. Consider upgrading to high-quality halogen or LED bulbs for improved visibility.
Taillights and Brake Lights:
Ensure taillights and brake lights are working correctly to signal your intentions to other drivers. Have someone help you check these lights while you press the brake pedal. Replace any bulbs that are not functioning, and inspect wiring for damage or corrosion.
Turn Signals:
Test turn signals and hazard lights to ensure they blink at the correct rate and are visible from all angles. Replace any bulbs that are dim or not flashing, and clean lenses regularly to maintain brightness. Consider upgrading to LED turn signal bulbs for faster response times and increased visibility.
5. Checking Brake Pads
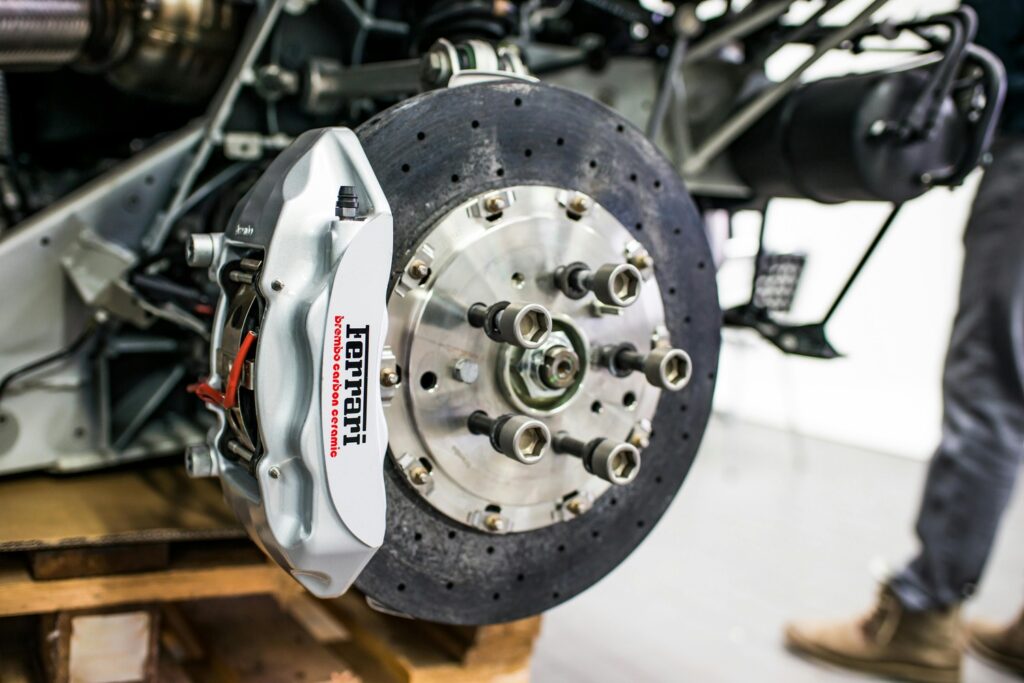

Properly functioning brakes are critical for safety and vehicle control:
Brake Pad Thickness:
Inspect brake pads for wear by looking through the wheel spokes or using a flashlight. Replace brake pads if the friction material is worn down to 3 millimeters or less. Signs of worn brake pads include squealing, grinding, or pulsating brakes.
Brake Fluid Level:
Check the brake fluid level in the master cylinder reservoir and top up if it’s low. Use the recommended brake fluid specified in your vehicle owner’s manual. Brake fluid absorbs moisture over time, leading to reduced braking performance and potential corrosion of brake components.
Brake System Inspection:
Inspect the entire brake system, including calipers, rotors, and brake lines, for leaks, corrosion, or damage. Address any issues promptly to ensure safe and reliable braking performance. Consider having the brake system inspected by a qualified mechanic as part of routine maintenance.
6. Cleaning Battery Terminals
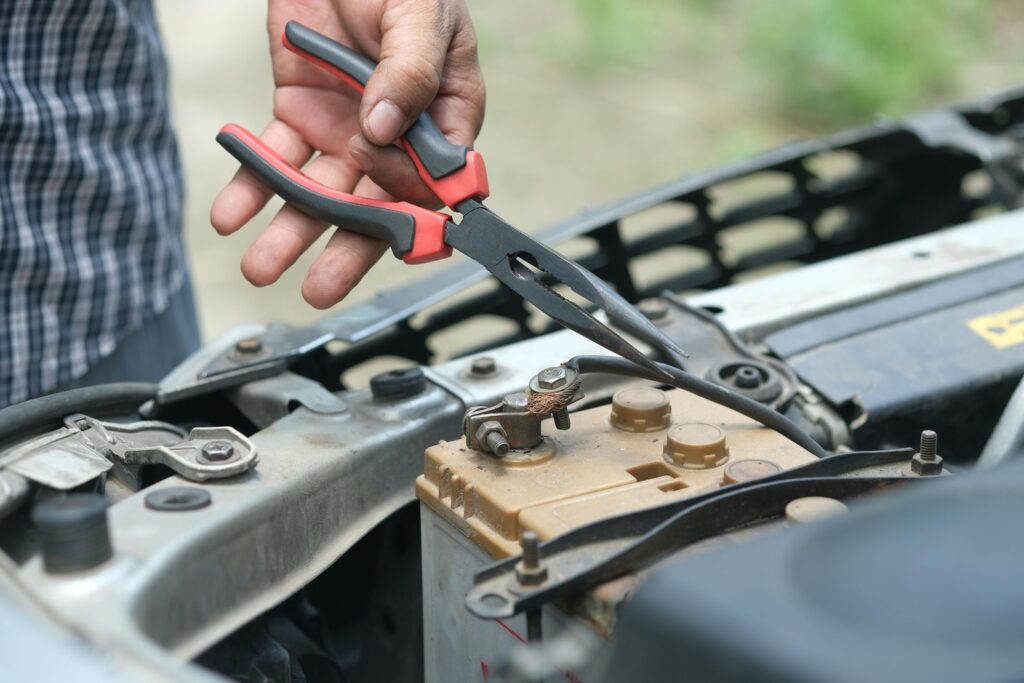

Corrosion on battery terminals can cause electrical problems and prevent the car from starting:
Cleaning Process:
Clean battery terminals with a mixture of baking soda and water to neutralize corrosion. Disconnect the battery cables and scrub the terminals with a wire brush. Rinse with water and dry thoroughly before reconnecting the cables. Apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
Battery Terminal Protection:
Prevent corrosion buildup by applying a commercial battery terminal protector or petroleum jelly to the terminals.
Inspect battery cables for fraying or damage, and replace them if necessary. Properly securing battery cables prevents accidental disconnection and ensures reliable electrical connections.
Battery Voltage Test:
Check the battery voltage with a multimeter to ensure it’s within the recommended range. A fully charged battery should measure around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is low, recharge the battery or have it tested by a professional. Weak or failing batteries can cause starting problems and electrical issues.
Battery Health Check:
Monitor battery health regularly using a battery tester or diagnostic tool. Test the battery’s cranking amps and reserve capacity to assess its overall condition. Replace the battery if it fails the test or shows signs of deterioration, such as slow cranking or frequent jump starts.
7. Inspecting Belts and Hoses
Belts and hoses play vital roles in your car’s operation, so inspect them regularly:
Drive Belts:
Inspect drive belts for signs of wear, cracks, or fraying. Replace worn or damaged belts promptly to prevent belt failure and engine damage. Check belt tension and adjust as needed according to your vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
Timing Belt:
Replace the timing belt at the recommended interval specified in your vehicle owner’s manual. A broken timing belt can cause catastrophic engine damage, so follow the manufacturer’s recommended replacement schedule. Consider replacing the water pump and other timing belt components at the same time for optimal performance.
Coolant Hoses:
Inspect coolant hoses for bulges, cracks, or leaks, especially around hose connections. Squeeze hoses gently to check for sponginess or brittleness, which indicates deterioration. Replace any hoses that show signs of wear to prevent coolant leaks or engine overheating.
Heater Hoses:
Check heater hoses for leaks or damage, especially in cold weather when the heating system is in use. Replace any heater hoses that show signs of wear to prevent coolant leaks inside the cabin. Properly functioning heater hoses ensure efficient heat transfer and comfortable driving conditions.
Power Steering Hoses:
Inspect power steering hoses for leaks, cracks, or damage, especially in high-temperature areas near the engine. Replace any power steering hoses that show signs of wear to prevent fluid leaks and steering system damage. Properly functioning power steering hoses ensure responsive steering and vehicle control.
8. Testing the Battery
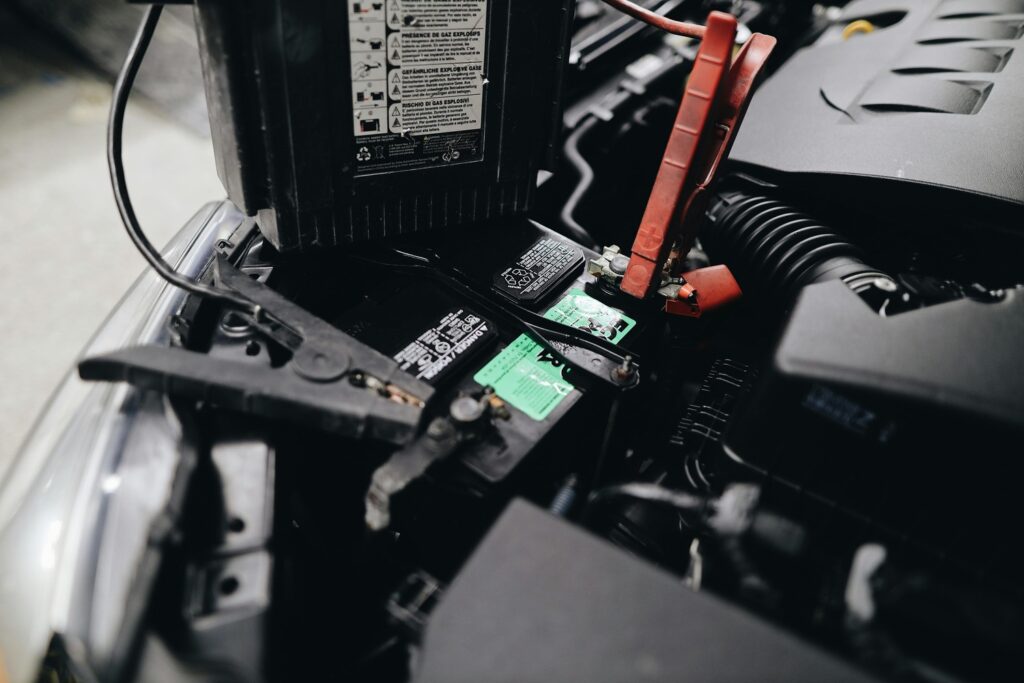

A weak or failing battery can leave you stranded, so test it regularly:
Voltage Test:
Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage when the car is off and when the engine is running. A healthy battery should measure around 12.6 volts when off and 13.7 to 14.7 volts when running. If the voltage is outside this range, recharge or replace the battery as needed.
Load Test:
Perform a load test on the battery to assess its cranking capacity and overall condition. A load tester applies a simulated load to the battery and measures its performance under load. Replace the battery if it fails the load test or shows signs of weakness, such as slow cranking or voltage drop.
Battery Terminal Inspection:
Inspect battery terminals for corrosion, loose connections, or damaged cables. Clean terminals with a wire brush and apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to prevent corrosion buildup. Ensure battery cables are tightly secured to the terminals to maintain reliable electrical connections.
Battery Health Monitoring:
Monitor battery health using a battery analyzer or diagnostic tool that measures internal resistance and conductance. Test the battery’s cold cranking amps and reserve capacity to assess its ability to start the engine and supply power to electrical systems. Replace the battery if it fails these tests or shows signs of deterioration.
9. Checking Windshield Wipers
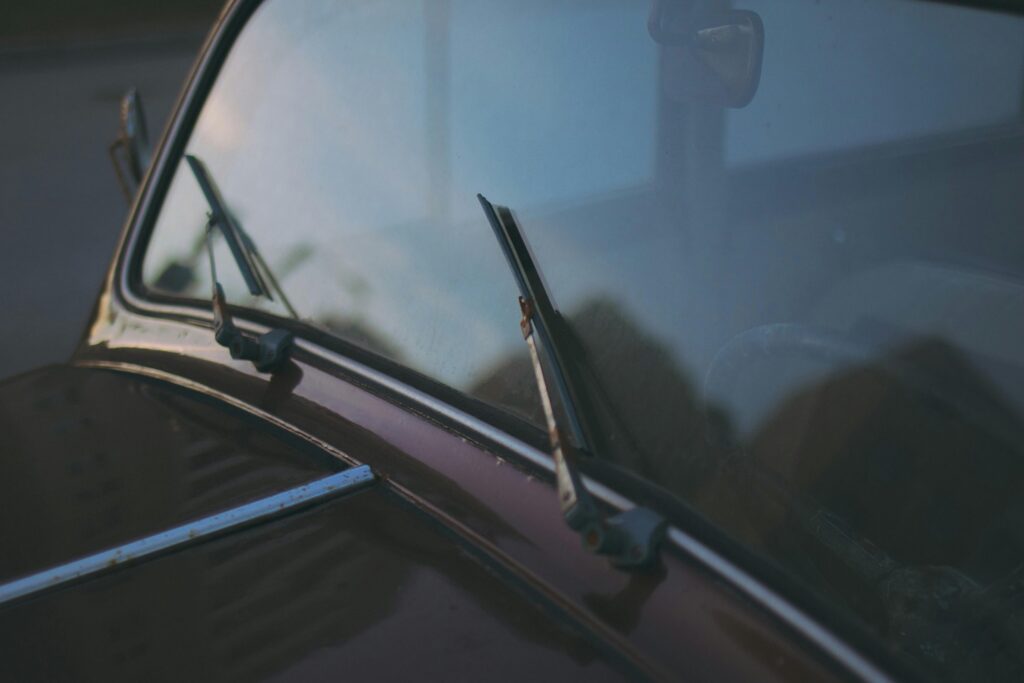

Clear visibility is essential for safe driving, so keep your windshield wipers in good condition:
Wiper Blade Inspection:
Inspect wiper blades for wear, cracks, or damage. Replace worn or damaged wiper blades to ensure effective windshield clearing during rain or snow. Check wiper arms for proper tension and adjust as needed to maintain even pressure across the windshield.
Washer Fluid Reservoir:
Keep the windshield washer fluid reservoir topped up with a mixture of water and windshield washer fluid. Use a funnel to fill the reservoir to the recommended level, especially before long trips or during winter months when road salt can quickly dirty the windshield.
Washer Nozzle Alignment:
Ensure washer nozzles are properly aligned to spray washer fluid onto the windshield. Use a pin or needle to adjust the direction of the spray if necessary. Clean nozzles regularly to remove dirt or debris that may block the flow of washer fluid.
Wiper Arm Maintenance:
Inspect wiper arms for rust, corrosion, or damage, especially at connection points. Lubricate wiper arm pivots with silicone spray or lithium grease to ensure smooth operation. Tighten wiper arm nuts or bolts to prevent wiper blade slippage or detachment while driving.
10. Maintaining Proper Wheel Alignment

Proper wheel alignment ensures even tire wear and optimal vehicle handling:
Alignment Inspection:
Have the wheel alignment checked regularly, especially after hitting potholes or curbs. Signs of misalignment include uneven tire wear, steering wheel vibration, or vehicle pulling to one side. Correcting alignment issues improves tire longevity and ensures safe driving.
Alignment Adjustment:
If wheel alignment is out of specification, have it adjusted by a qualified technician using specialized equipment. Proper alignment angles, including toe, camber, and caster, ensure even tire contact with the road surface and consistent vehicle stability. Follow your vehicle manufacturer’s alignment specifications for optimal performance.
Alignment Correction Methods:
Alignment adjustments may involve adjusting suspension components, such as tie rods, control arms, or strut mounts. Technicians use alignment racks and laser-guided tools to precisely adjust alignment angles to within manufacturer specifications. After alignment correction, test-drive the vehicle to ensure proper steering response and handling characteristics.
Alignment Maintenance:
Maintain proper wheel alignment by avoiding potholes, curbs, and other road hazards whenever possible. Regularly rotate tires and check tire pressure to promote even wear and prolong tire life. Inspect suspension components for wear or damage and address any issues promptly to prevent alignment problems.
11. Inspecting and Replacing Spark Plugs:
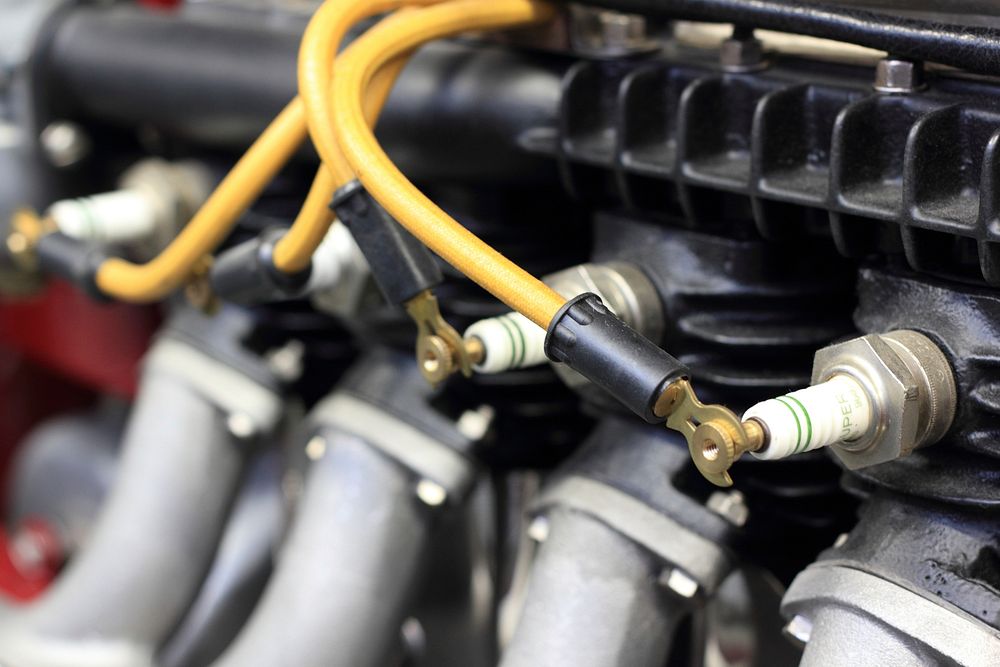

Spark plugs play a crucial role in your car’s ignition system, so keep them in good condition:
Spark Plug Inspection:
Remove and inspect spark plugs according to your manufacturer’s recommendations. Look for signs of wear, such as fouling, corrosion, or worn electrodes. Replace spark plugs if they show signs of deterioration to maintain optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Spark Plug Types:
Choose the appropriate spark plug type for your vehicle’s engine based on heat range, electrode configuration, and compatibility with ignition systems. Consult your vehicle owner’s manual or a trusted automotive technician for recommendations on spark plug selection and replacement intervals.
Spark Plug Gap Adjustment:
Ensure the spark plug gap is set to the correct specifications for your vehicle’s engine. Use a feeler gauge or spark plug gap tool to measure the gap between the electrodes and adjust as needed. Proper spark plug gap ensures optimal ignition timing and combustion efficiency.
Spark Plug Installation:
Install spark plugs carefully to avoid cross-threading or overtightening, which can damage cylinder head threads or crush the spark plug gasket. Apply a small amount of anti-seize compound to the spark plug threads to prevent corrosion and facilitate future removal. Tighten spark plugs to the specified torque using a torque wrench.
12. Testing the Air Conditioning System

A properly functioning air conditioning system is essential for comfort, especially during hot summer months:
AC Performance Test:
Test your air conditioning system by turning it on and checking for cool air coming from the vents. Monitor airflow and temperature settings to ensure proper cooling performance. If the air conditioner blows warm air or fails to cool adequately, have the system inspected by a qualified technician.
Cabin Air Filter Replacement:
Replace the cabin air filter regularly to maintain optimal airflow and air quality inside the vehicle. A dirty or clogged cabin air filter restricts airflow and reduces HVAC system efficiency. Follow your vehicle manufacturer’s recommendations for filter replacement intervals and filter type selection.
AC System Inspection:
Inspect the air conditioning system components, including the compressor, condenser, evaporator, and refrigerant lines, for leaks, damage, or wear. Check refrigerant levels and pressure using an AC manifold gauge set to diagnose system performance issues. Address any leaks or component failures promptly to prevent further damage.
AC System Maintenance:
Maintain your vehicle’s air conditioning system by operating it regularly, even during the winter months, to lubricate seals and prevent refrigerant leaks. Keep condenser coils and fins clean by rinsing them with water periodically to remove dirt, debris, and road grime. Consider scheduling annual AC system maintenance with a certified HVAC technician to ensure peak performance and reliability.
13. Inspecting the Exhaust System

The exhaust system plays a vital role in your car’s performance and emissions, so keep it in good condition:
Exhaust Inspection:
Visually inspect the exhaust system components, including the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, and exhaust pipes, for signs of rust, corrosion, or damage. Pay attention to exhaust leaks, rattling noises, or unusual odors that may indicate exhaust system problems.
Exhaust Leak Detection:
Detect exhaust leaks by listening for hissing or ticking noises under the vehicle while the engine is running. Use a mechanic’s stethoscope or a length of tubing to pinpoint the source of the noise along the exhaust system. Inspect exhaust gaskets, seals, and connections for leaks or damage.
Exhaust Emissions Testing:
Perform an exhaust emissions test to measure pollutant levels, including carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). Use a tailpipe emissions analyzer or visit a certified emissions testing facility to evaluate your vehicle’s exhaust emissions compliance. Address any emissions issues identified during testing to ensure environmental compliance and vehicle performance.
Exhaust System Maintenance:
Maintain your vehicle’s exhaust system by avoiding harsh driving conditions, such as excessive idling, stop-and-go traffic, or towing heavy loads, that can accelerate corrosion and exhaust system deterioration. Repair or replace damaged exhaust components, including mufflers, resonators, and exhaust pipes, to restore proper exhaust flow and minimize noise levels. Consider upgrading to high-quality stainless steel exhaust components for increased durability and corrosion resistance.
14. Keeping the Interior Clean

A clean interior not only looks better but also contributes to a healthier driving environment:
Interior Cleaning Tips:
Regularly vacuum carpets, floor mats, and upholstery to remove dirt, dust, and debris. Use a soft brush attachment or upholstery cleaner to loosen dirt and pet hair from fabric surfaces. Wipe down dashboard, door panels, and center console with a microfiber cloth and interior cleaner to remove dust and grime.
Carpet and Upholstery Stain Removal:
Treat carpet and upholstery stains promptly using a stain remover or carpet cleaner designed for automotive use. Blot spills with a clean cloth to absorb excess liquid, then apply the cleaner according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Use a soft brush to agitate the cleaner and lift stubborn stains before blotting dry.
Interior Odor Elimination:
Combat interior odors by using odor eliminators or air fresheners designed for automotive use. Choose products with neutralizing agents that eliminate odors rather than masking them with strong fragrances. Place odor eliminators in cupholders, under seats, or in the trunk to maintain a fresh-smelling interior.
Dashboard and Trim Care:
Protect and condition dashboard, door panels, and trim surfaces using a non-greasy interior protectant. Apply the protectant with a microfiber applicator pad or cloth, then buff to a matte finish to prevent glare. Avoid using silicone-based products that leave a shiny residue and attract dust.
15. Exterior Washing and Detailing

Regular exterior washing and detailing not only enhance your car’s appearance but also protect its paint and finish:
Hand Washing Techniques:
Wash your car by hand using a pH-balanced car wash soap and a soft sponge or microfiber wash mitt. Start from the top and work your way down, rinsing frequently to prevent soap residue from drying on the paint.
Use a separate sponge or wash mitt for wheels and tires to avoid cross-contamination.
Rinseless Wash Method:
Conserve water and minimize runoff by using a rinseless wash method with a waterless or rinseless wash solution. Dilute the wash solution according to the manufacturer’s instructions and apply it to the vehicle’s surface with a microfiber towel. Gently wipe and lift dirt from the paint, then buff dry with a clean microfiber towel.
Clay Bar Treatment:
Remove embedded contaminants and restore smoothness to the paint surface with a clay bar treatment. Lubricate the clay bar with a clay lubricant or quick detailer and gently glide it over the paint, glass, and chrome surfaces. The clay bar picks up contaminants and leaves behind a silky-smooth finish.
Polishing and Waxing:
Enhance paint gloss and depth by polishing and waxing the exterior surfaces. Use a dual-action polisher or orbital buffer to apply a non-abrasive polish to the paint, then buff to a high shine with a clean microfiber towel. Follow up with a coat of wax or paint sealant to protect the paint from UV damage and environmental contaminants.
By mastering these 15 essential car maintenance tasks, you can ensure your vehicle remains in optimal condition and operates reliably for years to come. Remember to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule outlined in the owner’s manual for specific intervals and procedures tailored to your vehicle model. With dedication and attention to detail, you’ll enjoy a smoother and safer driving experience on the road.

